Formation of a low-mass galaxy from star clusters in a 600-million-year-old Universe
L Mowla, K Iyer et al., Nature, volume 636, pages 332–336 (2024).
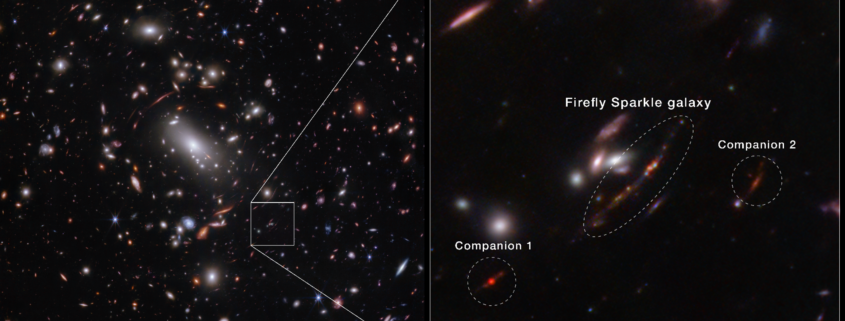
The most distant galaxies detected were seen when the Universe was a scant 5% of its current age. At these times, progenitors of galaxies such as the Milky Way were about 10,000 times less massive. Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) combined with magnification from gravitational lensing, these low-mass galaxies can not only be detected but also be studied in detail. Here we present JWST observations of a strongly lensed galaxy at zspec = 8.296 ± 0.001, showing massive star clusters (the Firefly Sparkle) cocooned in a diffuse arc in the Canadian Unbiased Cluster Survey (CANUCS). The Firefly Sparkle exhibits traits of a young, gas-rich galaxy in its early formation stage. The mass of the galaxy is concentrated in 10 star clusters (49–57% of total mass), with individual masses ranging from $10^5$ M$_\odot$ to $10^6$ M$_\odot$. These unresolved clusters have high surface densities ($>10^3$ M$_\odot$ pc$^{-2}$), exceeding those of Milky Way globular clusters and young star clusters in nearby galaxies. The central cluster shows a nebular-dominated spectrum, low metallicity, high gas density and high electron temperature, hinting at a top-heavy initial mass function. These observations provide our first spectrophotometric view of a typical galaxy in its early stages, in a 600-million-year-old Universe.

 NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Chris Willott (National Research Council Canada), Lamiya Mowla (Wellesley College), Kartheik Iyer (Columbia University)
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Chris Willott (National Research Council Canada), Lamiya Mowla (Wellesley College), Kartheik Iyer (Columbia University)

