Table of Contents
This is an old revision of the document!
4. Spring constant from extension and period
1. Introduction
Spring constant is a property of a spring; its value $k$ should be a constant. You will calculate $k$ using two different methods: first, using the extension $l$ caused by a hanging mass $m$ and second, using the period $T$ for a given hanging mass $m$.
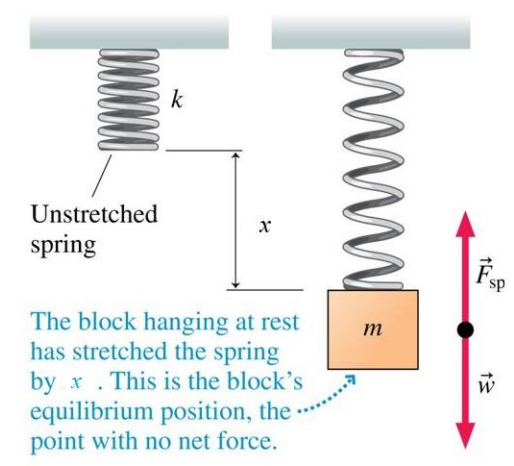
When a mass $m$ is hung from an unstretched spring, it is extended by a length $x=l$ because of the gravitational pull of the earth on the mass. The spring exerts a restoring force $F$ on the mass opposite to its gravitational force $mg$. According to Hooke’s law
$$ F \propto -l \Rightarrow F = -kl $$
where $k$ is the spring constant. Replacing $F=-mg$ we get $-mg = -kl $ and
$$ k = g\frac{m}{l}. $$
$$ l = \frac{g}{k}m + 0 $$
For the second method, you will use the relation between period and mass
$$ T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k'}} $$
which leads to
$$ k' = 4\pi^2 \frac{m}{T^2}. $$
The values $k$ and $k'$ should be very similar because they are both the spring constant of the same spring.
2. Method and data
| Mass $m$ [g] | Extension $l$ [cm] | Time for 10 oscillations $t$ [s] |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | ||
| 150 | ||
| 200 | ||
| 250 | ||
| 300 |
3. Spring constant from extension
4. Spring constant from period
5. Discussion and conclusion
- Why are $k$ and $k'$ different?
- Which one is greater, $\delta k$ or $\delta k'$? Why?
- In which method we have higher fitting error?
