Table of Contents
6. Temperature and heat
1. Zeroth law of thermodynamics

2. Temperature

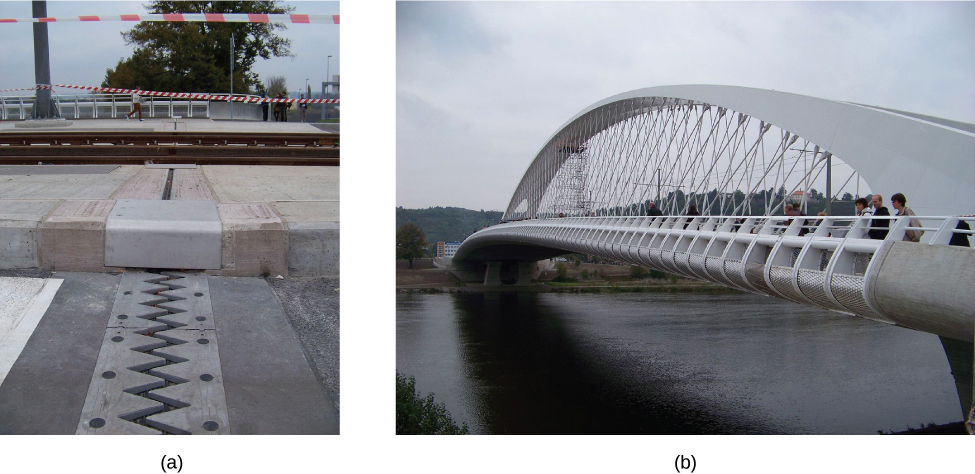
3. Thermal expansion

$$ \Delta L = \alpha L \Delta T $$
$$ \Delta V = \beta V \Delta T $$
$$ \beta = 3\alpha $$
$\alpha$ is coefficient of linear expansion, $\beta$ coefficient of volume expansion.

4. Heat
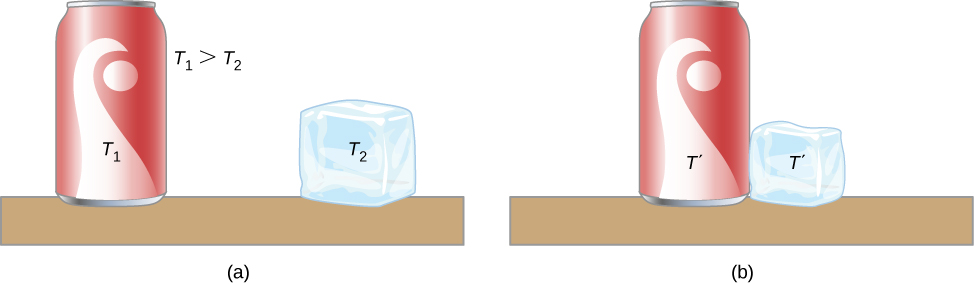

4.1 Heat capacity
$$ dQ = mc dT $$
Specific heat or specific heat capacity or just heat capacity
$$ c = \frac{1}{m}\frac{dQ}{dT} $$
Calorimetry:
$$ Q = mc \Delta T $$
$$ Q_c + Q_h = 0 $$
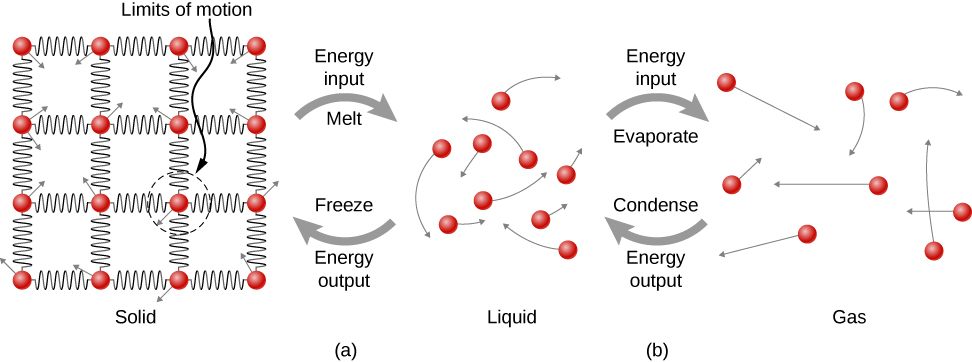
5. Phase changes

For fusion: $$ Q = m L_f $$
For evaporation: $$ Q = m L_v $$
$L_f$ is heat of fusion and $L_v$ heat of vaporization.

6. Heat transfer

6.1 Conduction

Rate of conductive heat transfer
$$ P = \frac{dQ}{dT} = -kA \frac{dT}{dx} $$
where $k$ is the thermal conductivity.
6.2 Convection

6.3 Radiation

The rate of radiated heat transfer
$$ P = \sigma A e T^4 $$
where $\sigma$ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant and $e$ the emissivity. If there is a surrounding,
$$ P_{net} = \sigma A e (T_2^4-T_1^4) $$

7. Ideal gas
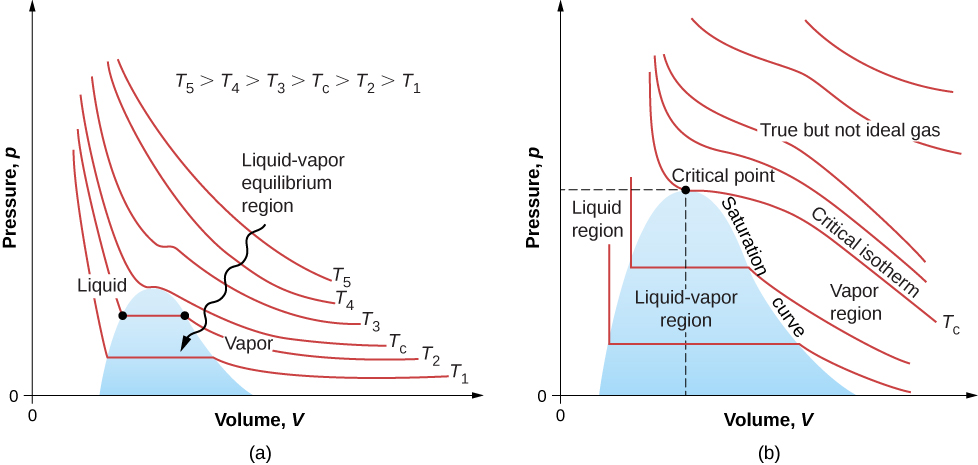
$$ pV = nRT = Nk_BT $$
$$ p = \rho k_BT $$
8. Kinetic theory of gas
Average kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas
$$ K = \frac{1}{2} mv^2 = \frac{3}{2} k_B T $$
Total internal energy of the gas
$$ E_{int} = NK = \frac{3}{2} Nk_BT = \frac{3}{2} nRT $$
RMS speed of a molecule
$$ v_{rms} = \sqrt{v^2} = \sqrt{\frac{3k_BT}{m}} $$